Cervical radicular pain or “cervical sciatica”.
What is
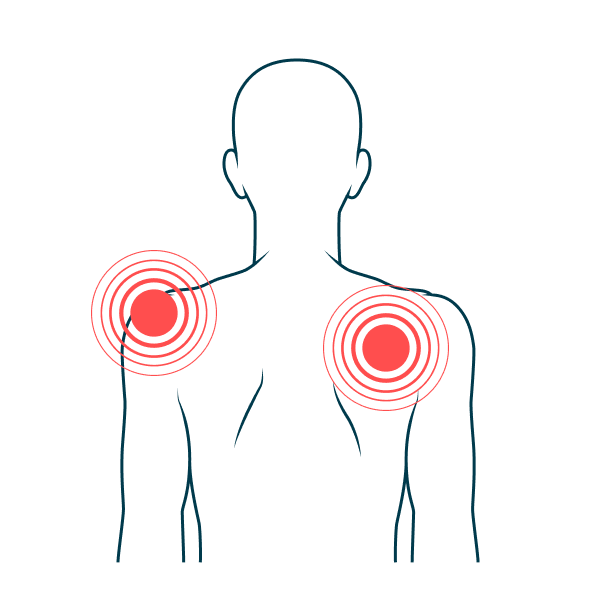
Radicular pain, or also commonly called sciatica (when it affects the legs) can also manifest itself in the upper limbs (arms). This pain, as in the legs, when it manifests itself in the arms, it manifests itself as a tingling, numbness or electric sensation that affects different areas. This pain can cause significant discomfort in the sufferer and may also be accompanied by alterations in motor skills. Determining the origin of the problem and where it is located is essential in order to apply the most appropriate treatment.
Causes
Generally this type of pain is produced as a consequence of the compression of one of the nerves that come out of the medulla to give sensory and motor capacity to the different parts of the upper limbs. Places where they can usually be compressed:
- Intervertebral disc (due to protrusion or herniation).
- Narrowing of the bony canal through which the nerves exit (known as the intervertebral foramen).
- Compression of the nerve at different points along its course from the medulla to its destination in the arm. The most frequent are the nerves at the level of the cervical musculature, at the level of the elbow compressing the ulnar nerve and at the level of the carpal tunnel in the wrist.
Symptoms
- Pain in different areas or regions of the arm / forearm or hand.
- Numbness sensation manifested in different areas of the arm/forearm or hand.
- Neuropathic symptoms such as a sensation of electricity or electric/ burning pain.
- All of these symptoms depending on where the nerve compression occurs can affect one part or more of the arm or both.

Our customers say
Insurance companies
Ask your MIVI centre for information on the agreements with insurance companies.